Fascinating Tidbits to Discover about Melatonin
Melatonin is a very interesting hormone!
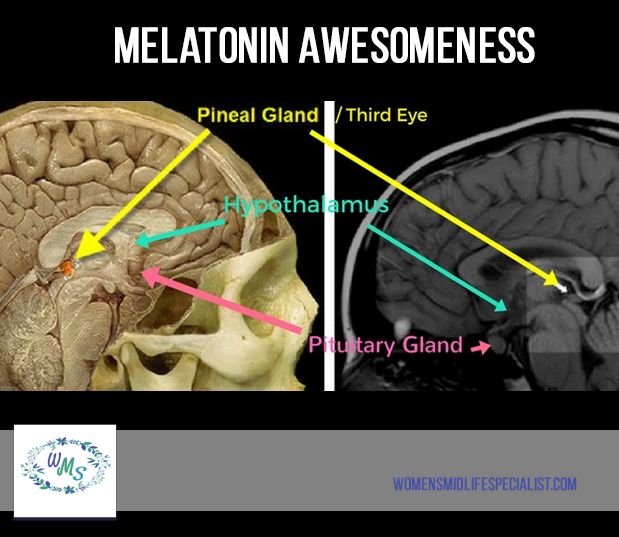
Pineal Gland ~ Our "Third Eye"
It is produced in a tiny gland, that is shaped like a pinecone, and no larger than a grain of rice. This gland is called the pineal gland and is also called our “third eye”. It sits in the center of the brain at the same level as the eyes and in close approximation to the hypothalamus and pituitary gland – very important areas associated with the regulation and production of all of our sex, thyroid, and adrenal hormones!
Most of us recognize Melatonin as our “sleep hormone”, and as important as this is, there’s even more Goodness to Melatonin that you really should know about!
Melatonin is the master of our entire internal body clock.
This internal body clock plays a role in our daily circadian rhythm, as well as our body’s monthly and seasonal rhythm!
That’s right! Melatonin helps regulate levels of Estrogen and Testosterone and thereby even helps regulate our menstrual cycles! It also helps regulate the frequency and duration of our periods!

Our Natural Circadian Rhythm
In addition to this master body clock regulator, Melatonin also plays a huge role in the function of our Immune System. Did you know that the brain isn’t the only place that Melatonin is produced? That’s right! Our Immune cells produce Melatonin as well – just like the pineal gland in the brain! And just like DHEA which plays a huge role in our immune system with DHEA receptor sites on almost all immune cells, Melatonin receptor sites are also present on almost every cell in our immune system. (No wonder our immune cells make their own Melatonin!)
When it comes to the actions of Melatonin in the immune cells, it is just a bit different than our hormone DHEA.
DHEA appears to UPregulate the immune system throughout the body – whereas Melatonin appears to act more as an “adaptogenic” hormone. That means it Up-regulates and Down-regulates – depending on what the body actually needs at that moment. Melatonin acts as an immune stimulant when you are in a suppressed state, (your immune system is not functioning at optimum), and the opposite – as a suppressant, when your immune system is in overdrive.
Melatonin Certificate of Awesome
Here is some more “Melatonin Awesomeness”!
Melatonin has been proven to decrease growth of bacterial, viral and parasitic infections!
Melatonin is also considered an antioxidant, helping take care of those nasty free radicals that can negatively affect our DNA.
Melatonin enhances the death of cancer cells during chemotherapy while protecting healthy cells.
Melatonin helps prevent rejection of organ transplantation.
Melatonin improves recovery from a stroke, reduces migraines, and helps decrease pressure in the eyes caused by glaucoma.
And Melatonin improves the functioning of the immune system even in the extreme elderly.

Melatonin Multiple Benefits
When it comes to Auto-immune disease, it is not as clear as to the different roles Melatonin plays and how Melatonin affects the body. We need more studies on the different Auto-immune conditions before we have a clear picture – probably since there is still so much yet to discover about how these conditions are set off in the first place.
However, a few things we do know about Melatonin and Auto-immune conditions is that it does appear to be beneficial for Type 1 diabetes, Systemic lupus (in women only), and in most studies Colitis. Interestingly these are the same Auto-immune conditions improved with Estrogen replacement.
When it comes to Rheumatoid Arthritis and Multiple sclerosis however, studies with Melatonin have shown mixed results – some beneficial, some negative and some with no change at all. Most Functional Medicine Doctors are leaning toward NOT using Melatonin in people with Rheumatoid Arthritis unless they have a sleep disorder and / or low Melatonin levels, because Melatonin suppresses Cortisol during the early morning hours. And Cortisol is responsible for decreasing inflammation – a hormone critically important for sufferers of Rheumatoid Arthritis. People who suffer from Rheumatoid Arthritis experience most joint pain first thing in the morning as the inflammatory fluids have settled within all of the joint spaces while they are sleeping and still. It is during the first hour after waking up and getting active that helps move this collected inflammatory fluid out of the joint spaces which helps give people with Rheumatoid Arthritis relief.
Now if you think all of this is pretty cool information, I’m not done! This is a big deal. I mean a REALLY big deal!
So how about one last little hint about Melatonin to help you the best I know how…. Melatonin levels plummet as we age just like all of our other hormones. And boy do I mean plummet. What we do produce during our midlife years is just a fraction of what we produced at our peak. And our Melatonin levels continue to decline the rest of our lives!

Melatonin Decline Through the Years
Melatonin actually comes originally from the amino acid Tryptophan. Tryptophan is then converted to 5 HTP, which is then converted to Serotonin. Finally, Melatonin is produced from Serotonin. Key nutrients are necessary to help carry out these enzymatic processes to make these different chemicals and hormones from Tryptophan, including magnesium, calcium Vitamin B6, Vitamin C, Folic acid, iron and zinc.

Melatonin Production
Here are additional key factors that reduce your own production of Melatonin and why most of us benefit from Melatonin supplementation.
Since the pineal gland secretes Melatonin based on the body’s natural body clock, if you lack a scheduled lifestyle, such as no regular bedtime or wake time, your body clock is poorly established, and the pineal gland has no idea of when to start or stop the production of Melatonin. Going to bed too late or sleeping during the day can be problematic.
In addition to this, the body’s natural rhythm also has a slight elevation “bump-up” in Cortisol around 11:00 p.m. and lasting for about 2-3 hours. If you are not in bed and asleep by 11:00 p.m. you may experience that “second wind” by being stimulated by this bump in cortisol level. Around 1:00 a.m. to 2:00 a.m. this slight elevating bump in Cortisol starts to decline again until it’s next scheduled rise around 6:00 – 7:00 a.m. when it normally does its job waking us up for the day.
Excessive stress in your life is detrimental to the production of Melatonin. As Melatonin increases, Cortisol decreases, and vice versa. So, you can see how chronic stress and its associated stimulation of Cortisol will inhibit your pineal gland’s secretion of Melatonin.
Drugs also play a factor in the production of Melatonin. Aspirin is a common over the counter medication used by many that has been shown to decrease Melatonin production. There are also certain prescription medications known to decrease your body’s ability to produce Melatonin. These include Benzodiazepines such as Xanax, Ativan and Valium. Diuretics such as Lasix and Bumex and Beta blockers such as Metoprolol, carvedilol, and propranolol also decrease your body’s ability to make Melatonin.

Drugs that Decrease Melatonin Production
And as you would guess, since you now know Melatonin comes from the amino acid Tryptophan requiring additional nutrients such as Vitamin B6, Vitamin C, magnesium, calcium iron and folate, and zinc, lacking any one of these nutrients will prevent your pineal gland from producing Melatonin.
One last additional key factor for Melatonin production is how much light you are exposed to both during the day and after dark. Your body’s cycle needs light during the day and dark during the night. Too much light at night decreases Melatonin and too little light during the daytime will also decrease Melatonin. People who live in northern latitudes, and those who tend to spend excessive time indoors during the day, will produce less Melatonin.
In addition, exposure to blue light 1-2 hours before bed will also severely suppress Melatonin. (White and Green lights also suppress Melatonin 1-2 hours before bed, but blue is the most detrimental to your pineal gland.) Blue light comes from the TV screens, computer screens, and phone screens! And as you know, these are what so many of us are glued to right up until the moment we go to bed. Many of us even have TV’s on in our bedroom!
Here’s the good part. Melatonin doesn’t seem to be as suppressed with Red light. So red bedside table lamps and nightlights are good places to use Red light bulbs. Red lights can be romantic too… so give it a try! And since Melatonin is also affected by the actual brightness of the light, make sure you get a low watt red light – about 7.5 to 10 watts for your bedside table and 5 watts or less for night lights.

Melatonin's Sensitivity to Light
So, as you see, it’s not just about the natural decline of Melatonin as we age that results in inadequate Melatonin production. All of these factors, which are often quite common in today’s lifestyle, play a substantial role in Melatonin production.


Leave a comment